The Feline Frontier: Cats in Space and the Quest for Cosmic Companionship
- 11 Comments
In a groundbreaking and truly out-of-this-world development, cats are set to embark on space missions as part of an innovative project aimed at exploring the potential for interspecies companionship in extraterrestrial environments. While dogs have historically been the pets of choice for many astronauts, the unique qualities of cats could make them ideal companions for long-duration space missions.
The concept of taking cats to space is not entirely new. In 1963, a French cat named Félicette became the first and only feline to travel to space, successfully returning to Earth after a brief mission that provided valuable data on the neurological responses to space travel. However, the idea of incorporating cats into space missions as bona fide crew members has gained traction in recent years, thanks to advancements in space travel technology and an increased understanding of feline behavior and needs.
Cats possess several characteristics that make them well-suited for space travel. Their small size and low maintenance requirements mean they take up minimal space and need fewer resources than larger animals. Additionally, their independent nature allows them to adjust to changes in their environment with relative ease. Unlike dogs, who may require more attention and interaction, cats are known for their ability to entertain themselves, making them ideal candidates for the isolated conditions of space travel.
Researchers involved in the project have been conducting studies to understand how the zero-gravity environment of space affects cats. Preliminary findings suggest that cats quickly adapt to weightlessness, often exhibiting playful and curious behaviors as they explore their new surroundings. This adaptability could provide much-needed psychological support for astronauts on long missions, offering a source of joy and companionship that can alleviate the stress and monotony of life in space.
The potential benefits of having cats aboard spacecraft extend beyond emotional support. Cats have been known to respond to the presence of pests, making them valuable for maintaining the cleanliness of living quarters. In a closed environment such as a spacecraft, where cleanliness is paramount, the natural hunting instincts of cats could prove beneficial in controlling any unexpected pest issues.
As part of the preparatory phase, selected cats are undergoing rigorous training to acclimate them to the conditions they will face in space. This includes exposure to simulated microgravity environments, loud noises, and the confined spaces of a spacecraft. The training aims to ensure that the cats are comfortable and well-adjusted, reducing the likelihood of stress-related behaviors during the mission.
The inclusion of cats in space missions also raises important ethical considerations. Animal welfare organizations have expressed concerns about the well-being of cats in such extreme conditions. To address these concerns, the project has implemented strict guidelines to ensure the safety and health of the feline participants, including regular health checks and monitoring of their physical and mental well-being.
As humanity looks toward establishing a presence on other planets, the role of animals in these endeavors cannot be overlooked. The involvement of cats in space missions marks a new chapter in our relationship with these enigmatic creatures, pushing the boundaries of our understanding and cooperation. Whether cats will become a common sight on future space missions remains to be seen, but their potential contribution to the success and well-being of astronauts is undeniable.
The Feline Frontier is an exciting exploration of the possibilities that lie ahead as we continue to reach for the stars. As cats prepare to join humans on this cosmic journey, their presence in space could redefine the parameters of companionship and collaboration beyond Earth, opening up new horizons for both species.
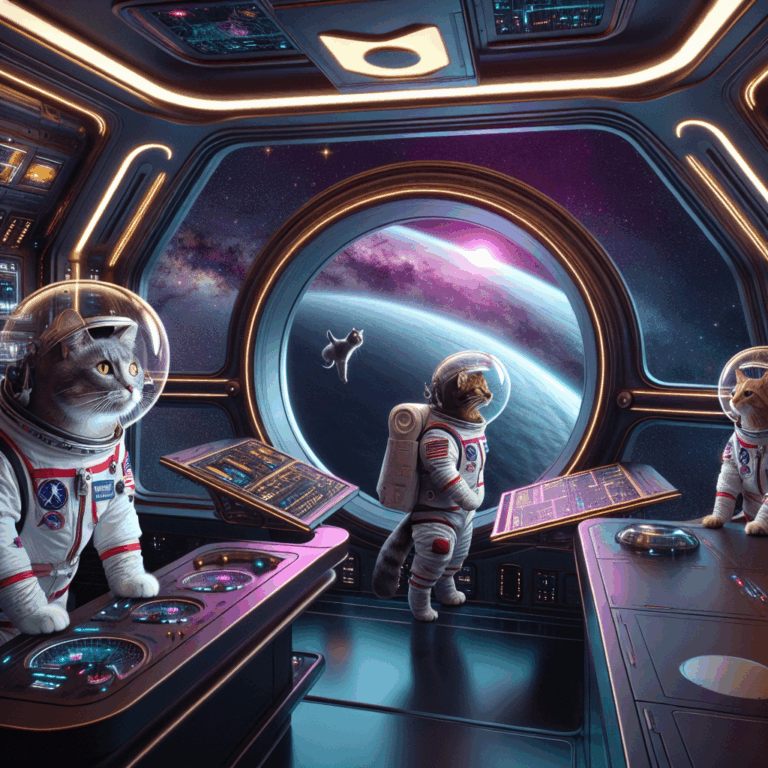
In a groundbreaking and truly out-of-this-world development, cats are set to embark on space missions as part of an innovative project aimed at exploring the potential for interspecies companionship in extraterrestrial environments. While dogs have historically been the pets of choice for many astronauts, the unique qualities of cats could make them ideal companions for long-duration space missions.
The concept of taking cats to space is not entirely new. In 1963, a French cat named Félicette became the first and only feline to travel to space, successfully returning to Earth after a brief mission that provided valuable data on the neurological responses to space travel. However, the idea of incorporating cats into space missions as bona fide crew members has gained traction in recent years, thanks to advancements in space travel technology and an increased understanding of feline behavior and needs.
Cats possess several characteristics that make them well-suited for space travel. Their small size and low maintenance requirements mean they take up minimal space and need fewer resources than larger animals. Additionally, their independent nature allows them to adjust to changes in their environment with relative ease. Unlike dogs, who may require more attention and interaction, cats are known for their ability to entertain themselves, making them ideal candidates for the isolated conditions of space travel.
Researchers involved in the project have been conducting studies to understand how the zero-gravity environment of space affects cats. Preliminary findings suggest that cats quickly adapt to weightlessness, often exhibiting playful and curious behaviors as they explore their new surroundings. This adaptability could provide much-needed psychological support for astronauts on long missions, offering a source of joy and companionship that can alleviate the stress and monotony of life in space.
The potential benefits of having cats aboard spacecraft extend beyond emotional support. Cats have been known to respond to the presence of pests, making them valuable for maintaining the cleanliness of living quarters. In a closed environment such as a spacecraft, where cleanliness is paramount, the natural hunting instincts of cats could prove beneficial in controlling any unexpected pest issues.
As part of the preparatory phase, selected cats are undergoing rigorous training to acclimate them to the conditions they will face in space. This includes exposure to simulated microgravity environments, loud noises, and the confined spaces of a spacecraft. The training aims to ensure that the cats are comfortable and well-adjusted, reducing the likelihood of stress-related behaviors during the mission.
The inclusion of cats in space missions also raises important ethical considerations. Animal welfare organizations have expressed concerns about the well-being of cats in such extreme conditions. To address these concerns, the project has implemented strict guidelines to ensure the safety and health of the feline participants, including regular health checks and monitoring of their physical and mental well-being.
As humanity looks toward establishing a presence on other planets, the role of animals in these endeavors cannot be overlooked. The involvement of cats in space missions marks a new chapter in our relationship with these enigmatic creatures, pushing the boundaries of our understanding and cooperation. Whether cats will become a common sight on future space missions remains to be seen, but their potential contribution to the success and well-being of astronauts is undeniable.
The Feline Frontier is an exciting exploration of the possibilities that lie ahead as we continue to reach for the stars. As cats prepare to join humans on this cosmic journey, their presence in space could redefine the parameters of companionship and collaboration beyond Earth, opening up new horizons for both species.


11 thoughts on “The Feline Frontier: Cats in Space and the Quest for Cosmic Companionship”
This innovative initiative highlights promising opportunities for interspecies collaboration in space exploration.
It’s exciting to see the potential for interspecies collaboration being explored in space missions. This initiative could bring about new insights and enhance the experience of astronauts during long-duration spaceflights.
This innovative project is a fascinating step forward in exploring companionship possibilities beyond Earth.
This is an intriguing exploration of how cats could enhance space missions with their unique qualities.
What an intriguing exploration of the potential for feline companionship in space missions!
This article provides an interesting perspective on the potential benefits and challenges of including cats in future space missions.
It’s exciting to see how feline companions might enhance space missions with their unique characteristics and adaptability.
This innovative initiative highlights the exciting potential for interspecies companionship in space exploration.
This fascinating development highlights the potential for cats to bring joy and companionship to astronauts on their cosmic journeys.
This innovative project highlights the exciting potential for enhancing astronaut experiences with feline companions in space.
It’s fascinating but seems implausible that cats, with their unique behavioral needs, would be ideal companions for space missions.