The Feline Innovators of Medical Advancements: Cats and Their Surprising Role in Healthcare
- 9 Comments
In the realm of healthcare, where innovation and discovery are paramount, an unexpected contributor has silently played a role in numerous medical advancements: the domestic cat. Known for their agility, independence, and mysterious nature, cats have been integral in shaping various aspects of modern medicine, often in ways that go unnoticed by the general public.
The history of cats in medical research dates back centuries, with their physiology being studied to understand human diseases better. Their unique immune system, for instance, has provided insight into the treatment of autoimmune disorders. Feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV), a virus similar to HIV in humans, has been instrumental in helping researchers develop antiretroviral therapies that have saved countless lives. The study of FIV continues to inform the development of vaccines and treatments for HIV, showcasing the pivotal role that cats play in the ongoing battle against this global epidemic.
Moreover, the sensory capabilities of cats have been harnessed in diagnostic technologies. Their acute sense of smell, often compared to that of canines, is being explored for its potential in detecting diseases such as cancer. Recent studies have shown that cats can identify changes in human body chemistry, which could lead to the development of non-invasive diagnostic tools that rely on scent detection.
In the field of neurology, cats have been at the forefront of understanding complex brain functions. Their cerebral anatomy and neural pathways have provided a model for studying epilepsy, sleep disorders, and even neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. The feline brain shares several similarities with the human brain, making it an invaluable subject for neuroscientific research. This has led to breakthroughs in treatments and therapies that improve the quality of life for patients with neurological conditions.
Cats have also contributed to the field of regenerative medicine. Their remarkable ability to heal from injuries with minimal scarring has piqued the interest of scientists looking to apply similar principles to human tissue regeneration. The study of feline genetics related to wound healing is paving the way for advancements in regenerative therapies, potentially revolutionizing the way we approach recovery from surgeries and injuries.
Beyond their biological contributions, cats have a profound impact on mental health, a critical component of holistic healthcare. The presence of a cat has been shown to reduce stress and anxiety, leading to improved mental well-being. This connection has fueled the growth of animal-assisted therapy programs, where cats are used to provide comfort and companionship to patients in hospitals, nursing homes, and rehabilitation centers. The calming influence of cats can enhance patient outcomes, highlighting their therapeutic value in medical settings.
As the medical community continues to explore the potential of feline contributions, it is essential to recognize and celebrate the unique role that cats play in advancing healthcare. From aiding in groundbreaking research to providing emotional support, these enigmatic creatures have proven to be more than just beloved pets. They are silent partners in the quest for knowledge and healing, reminding us of the interconnectedness of all living beings in the pursuit of health and well-being.
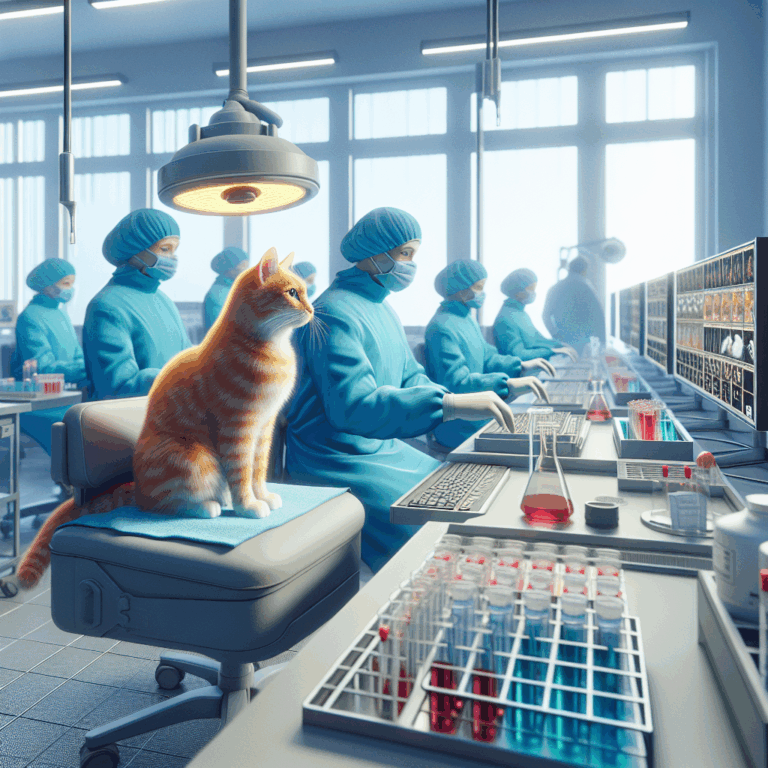
In the realm of healthcare, where innovation and discovery are paramount, an unexpected contributor has silently played a role in numerous medical advancements: the domestic cat. Known for their agility, independence, and mysterious nature, cats have been integral in shaping various aspects of modern medicine, often in ways that go unnoticed by the general public.
The history of cats in medical research dates back centuries, with their physiology being studied to understand human diseases better. Their unique immune system, for instance, has provided insight into the treatment of autoimmune disorders. Feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV), a virus similar to HIV in humans, has been instrumental in helping researchers develop antiretroviral therapies that have saved countless lives. The study of FIV continues to inform the development of vaccines and treatments for HIV, showcasing the pivotal role that cats play in the ongoing battle against this global epidemic.
Moreover, the sensory capabilities of cats have been harnessed in diagnostic technologies. Their acute sense of smell, often compared to that of canines, is being explored for its potential in detecting diseases such as cancer. Recent studies have shown that cats can identify changes in human body chemistry, which could lead to the development of non-invasive diagnostic tools that rely on scent detection.
In the field of neurology, cats have been at the forefront of understanding complex brain functions. Their cerebral anatomy and neural pathways have provided a model for studying epilepsy, sleep disorders, and even neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. The feline brain shares several similarities with the human brain, making it an invaluable subject for neuroscientific research. This has led to breakthroughs in treatments and therapies that improve the quality of life for patients with neurological conditions.
Cats have also contributed to the field of regenerative medicine. Their remarkable ability to heal from injuries with minimal scarring has piqued the interest of scientists looking to apply similar principles to human tissue regeneration. The study of feline genetics related to wound healing is paving the way for advancements in regenerative therapies, potentially revolutionizing the way we approach recovery from surgeries and injuries.
Beyond their biological contributions, cats have a profound impact on mental health, a critical component of holistic healthcare. The presence of a cat has been shown to reduce stress and anxiety, leading to improved mental well-being. This connection has fueled the growth of animal-assisted therapy programs, where cats are used to provide comfort and companionship to patients in hospitals, nursing homes, and rehabilitation centers. The calming influence of cats can enhance patient outcomes, highlighting their therapeutic value in medical settings.
As the medical community continues to explore the potential of feline contributions, it is essential to recognize and celebrate the unique role that cats play in advancing healthcare. From aiding in groundbreaking research to providing emotional support, these enigmatic creatures have proven to be more than just beloved pets. They are silent partners in the quest for knowledge and healing, reminding us of the interconnectedness of all living beings in the pursuit of health and well-being.


9 thoughts on “The Feline Innovators of Medical Advancements: Cats and Their Surprising Role in Healthcare”
It’s fascinating to learn about the unexpected ways cats contribute to medical advancements and healthcare.
It truly is intriguing to see how cats play a role in medical advancements, from aiding in research to enhancing mental well-being. Their contributions often go unnoticed, yet they have a significant impact on healthcare.
// This insightful post highlights the crucial contributions of cats to medical advancements in a fascinating way!
It’s fascinating to learn about the significant contributions cats have made to medical research and healthcare advancements.
It’s indeed intriguing how cats have played such a crucial role in medical research and healthcare. Their unique qualities continue to inspire and lead to valuable discoveries.
While the article highlights fascinating contributions of cats to medical research, it seems to overlook the ethical concerns associated with using animals in scientific studies.
This post sheds light on the fascinating contributions of cats to healthcare, highlighting their unexpected and valuable role in medical advancements.
While the article highlights intriguing points about cats in medical research, it tends to overstate their contributions. For instance, while FIV research has provided insights, it’s human-focused studies that drive major HIV advancements. Additionally, the claims about cats’ diagnostic abilities and their impact on neurodegenerative research seem speculative without robust evidence. More scientific rigor is needed to substantiate these claims.
You bring up important considerations about the need for robust scientific evidence in medical research. It’s fascinating to see how cats have contributed in various ways, and future studies could further clarify their role. The potential for new discoveries in both feline and human health is certainly exciting!